Search
-
Prevent Osteoporosis: Take Control of Your Bone Health Today
Some risk factors associated with osteoporosis are out of your control. But you’re in luck, because some can be lessened by following simple tips. Below, Orthopedic Nursing Manager Katie McCarthy discusses the signs, symptoms and preventive measures. By Katie McCarthy, BSN, RN, ONC, Orthopedic Nursing Manager, Renown Health Osteoporosis is often called the silent disease, because it develops gradually for years with no clear signs or symptoms. And while some bone loss is expected as we age, osteoporosis is not a normal part of aging. So it’s important to start thinking about your bone health early. Bone is not just a lifeless scaffold for the body. It is living tissue that regenerates continually. Once we reach peak bone mass around age 25, we begin losing more bone than we produce, increasing the risk of developing osteoporosis — which literally means porous bone and points to a loss in bone density. In severe cases, normal everyday activities or movements, like hugging, can cause a fracture. After the first fracture you’re at higher risk for more, which can lead to a life of chronic pain and immobility. Bone fractures in the spine or hip are the most serious. Hip fractures can result in disability and even death — especially in older adults. Spinal fractures can even occur without falling. The vertebrae weaken to the point that they simply crumple, which can result in back pain, lost height and a hunched-forward posture. Osteoporosis: Uncontrollable Risk Factors Women are at greater risk of developing osteoporosis than men, and white and Asian women are at higher risk than black and Hispanic women. Other uncontrollable risk factors include: age; a family history of osteoporosis; certain genetic conditions; medications and medical treatments; eating disorders; a low body weight and small, thin frame; ethnicity; menopause: In fact, the lack of estrogen produced during menopause is largely responsible for a woman’s increased risk. Poor diet, tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, lack of exercise and an unhealthy weight also contribute to bone loss. Fortunately, those risk factors are in your control. Without symptoms, you can’t know if you’ve developed osteoporosis unless you get a bone density test or suffer a fracture. If you fall into a high-risk group, are over age 50 or have any concerns about your bone health, consult your doctor and find out if you need to be evaluated. Additionally, if either of your parents sustained hip fractures, you experienced early menopause or took corticosteroids for several months — a steroid often prescribed to relieve inflammation and arthritis — you’ll want to talk to your doctor about your bone health. If you test positive, your doctor will devise a treatment plan to match your needs, which will include lifestyle changes surrounding diet and exercise to build and strengthen weak bones. Medication to slow bone breakdown and build new bone may be prescribed, depending on the severity of your bone loss. If you’ve sustained a spinal fracture that is causing severe pain, deformity or is not responding to non-surgical treatment, your doctor may recommend surgery. Reduce Your Risk of Osteoporosis You can strengthen your bones now to prevent osteoporosis from starting. Here are some tips: Eat a diet rich in fruits and vegetables and low in caffeine, sodium and protein. Avoid soda, and talk to your doctor to make sure you’re getting enough calcium and vitamin D. Don’t smoke — it directly correlates with a decrease in bone mass. Smokers also take longer to heal from a fracture. Limit alcohol to two to three beverages per day. It interferes with the production of vitamins needed to absorb calcium and the hormones that help protect bones. Exercise three to four times each week — it’s key to healthy bones. Weight-bearing exercises like jogging, hiking and especially weight lifting build bone mass and density. There are aspects of the aging process we can’t control, but we can do something about bone loss and osteoporosis. Find out your risk, and show your bones a little TLC — you’re going to need them. This story was also published in the Reno Gazette-Journal’s Health Source on April 24, 2016.
Read More About Prevent Osteoporosis: Take Control of Your Bone Health Today
-
A True Joint Effort: Exercises to Prevent Knee Pain
Experiencing knee pain during exercise or while undertaking daily activities? The knee is the largest joint in our body, so it goes without saying a lot hinges on its functionality. Here are a few exercises to help. Is exercise a real pain in the knee for you? Does getting up in the morning require a few minutes for your knees to adjust to walking around? As it turns out, knee pain is common, and it can result from injury, overuse or the breakdown of cartilage over time. Often, this pain is a result of faulty mechanics in your body, according to Jessica Ryder, a physical therapist with Renown Physical Therapy and Rehab. “We see weakness at the hips causing a lot of stresses at the knee,” she says. Exercises that Alleviate Knee Pain Try these three exercise to strengthen your glute muscles and maintain proper alignment in your knees. Hip Lift Lie flat on your back with your knees bent and feet flat against the floor. Lift your hips into the air until your body is in a neutral position, then lower your hips back down. Repeat this motion several times until you feel a gentle burn in your glute muscles. Step Down Stand with one foot on a stair or step. Slowly bend your knee and drop the other foot toward the floor. Slowly extend back up to your starting position. While doing this exercise, it’s important to move slowly, maintain control and ensure that your knee is in line with your toes. Do as many reps as needed until you feel a small fatigue in your muscles. Repeat this exercise on the opposite leg. Side Step with Exercise Band Place an exercise band around your ankles. Stand in a slight squat and then take several steps to the side until you feel a small fatigue on the outside of your hips. While doing this exercise, keep your upper body still and focus the exercise to your hips. The band will try to move your knees toward each other Repeat in both directions. Hometown Health and Renown Health are proud to be the official insurance plan and healthcare partners of the Nevada Wolf Pack. Renown Physical Therapy and Rehab | 775-982-5001 Through outpatient physical, occupational and also speech therapy, Renown Physical Therapy and Rehab gives patients hands-on, individualized treatment. Our therapists use evidence-based methods to help patients return to an active, productive lifestyle. Learn More About PT
Read More About A True Joint Effort: Exercises to Prevent Knee Pain
-
Six Tips for Healthy Vision
You might think worsening eyesight is inevitable as you age. But the truth is, there are easy things you can do to keep your eyes in tiptop shape for years to come. Clear vision is an essential part of overall health and there are daily habits we can adopt to keep our eyes seeing clearly. Mitchell Strominger, M.D., a registered ophthalmologist with Renown Health specializing in pediatric ophthalmology and neuro-ophthalmology, offers some everyday tips to keep you focused on eye health. Know your family’s vision history Look to your parents and grandparents for clues about the future of your eye health. Were they near-sighted at a young age? Do they have a history of eye crossing or a lazy eye? Did they develop glaucoma or macular degeneration (AMD)? Some genes have a strong association with eye health, specifically macular degeneration. AMD is a leading cause of blindness worldwide and the top cause of vision loss and blindness for Americans over 65, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Also be aware certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, high blood pressure and liver disease, increase the risk of long-term eye problems. Receive regular vision screening exams Children under three need vision screening examinations by their pediatrician. A medical concern or family history warrants a comprehensive eye examination by a pediatric ophthalmologist (or general ophthalmologist or optometrist who has experience with children) per the American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO). Vision screenings should occur every two years throughout adolescence unless pain, eye crossing, difficulty seeing the board or reading, or other eye concerns occur. In adulthood the risk of eye problems increases over age 40, so the AAO recommends regular dilated exams. When your pupils are dilated it allows your eye care professional a more accurate view of your retina and optic nerve, located in the back of your eye. This allows them to look for AMD or other eye problems. Eye diseases can be caught at their earliest stages during a dilated eye exam. “It is especially important to have your child evaluated as soon as possible if there is any concern for eye crossing or lazy eye,” says Dr. Strominger. “The visual system develops in the early years so intervention, whether it be glasses, eye patching to strengthen the vision in one eye, or eye muscle surgery is critical. Children at risk include those who are born premature, have development abnormalities, genetic disorders such as Downs syndrome, or a strong family history and should be evaluated at a young age. Often small problems are not clearly evident and cannot be picked up on routine screening examinations in the pediatrician’s office.” Block the sun, improve your vision Everyone knows not to stare directly into the sun, but indirect ultraviolet (UV) sun rays can cause serious harm over time. According to the National Eye Institute, sunglasses (or a protective UV tint) are a daily must to protect your eyes from: Cataracts (a clouding of the eye’s lens causing blurred vision) AMD - macular degeneration Pterygium (a tissue growth over the white surface of the eye that can cause astigmatism) Look for sunglasses which block 99 to 100 percent of both UVA and UVB rays. You still need sunglasses if your contact lenses block UV rays. Sun rays can damage your eyelids and other tissue not covered by contact lenses. Wearing sunglasses protects your entire eye area. Eat colorful meals Your eyes need vital nutrients to keep them healthy including vitamin C, zinc, beta carotene and copper. A diet filled with citrus fruits and a variety of vegetables provide these essential nutrients. Regularly filling up on fish high in omega-3 fatty acids (salmon, tuna, sardines) may reduce your risk of AMD and help maintain your eye health. Green, leafy vegetables (kale, spinach, collard greens) containing lutein and zeaxanthin are also a must for your dinner plate. Water your eyes Eyes, like the rest of your body, need plenty of water to prevent dehydration. Make sure you stay hydrated and steer clear of smoke to avoid dry eyes and irritation. Hours staring at the computer screen can also make your eyes feel dry or tired. Try regularly refreshing them with lubricating eye drops. Taking frequent computer breaks is also important. Follow the 20/20/20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at an object 20 feet away from you for 20 seconds. Eye makeup can also lead to dry eye as the glands at the base of the eyelashes may become clogged, causing dry eye. Make sure all eye makeup is hypoallergenic and is thoroughly removed with a gentle cleanser for the delicate eye area each day. Stop Smoking (or never start) Smoking is harmful to every part of your body, including your eyes. It's not only linked to cancer and heart disease but also cataracts, AMD, dry eye, optic nerve problems and many other problems. Smoking during pregnancy can also harm the eyes of the unborn child. If you currently smoke take steps to quit and your entire body will benefit.
-
Bone Fractures in Children Honest Expert Advice
Michael Elliott, MD, head of the Department of Pediatric Orthopedics and Scoliosis, answers some common questions about bone fractures. Is there a difference between broken bones and fractures? No, these are two different names for the same injury. Of course the common term is a broken bone. Using either name will describe your concerns. Medical personnel typically describe a broken bone as a fracture to a specific bone. For example, a broken wrist is also a fractured distal radius. To clarify, this describes the injured bone and the precise location. How do I know if my child has broken their bone? Many times children will fall and complain of their arm or leg hurting. In most cases the pain goes away and the child will return to their activities. When there is a deformity to the limb (curve in arm) and the child is complaining of pain, it is probably a fracture. If the arm or leg looks straight, look to see if there is any swelling or bruising. Both are signs of a possible fracture. Finally, if the limb looks normal but the child continues to complain, gently push on the bone. Likewise if it causes the same pain, then they likely have a fracture and should have an x-ray. My child fractured their growth plate, what does this mean? Growth comes from this area of the bone. In detail, these are located all over the body but typically at the end of the bones. With this in mind, fractures to these areas can result in the bone growing abnormally. Because of potential shortening of the arm or leg, or bones growing crooked, it is important to follow fractures closely (up to 1-2 years or longer). It is better to identify a problem early. Small problems can be treated with small surgeries. What if the bones of the x-ray do not line up? Because children are growing, unlike adults, their bones will remodel and straighten with growth. The amount of remodeling occurring depends on a child’s age, the bone fractured and the location. In many cases an angled bone will grow straight over the course of a year. For this reason, someone with experience in caring for children needs to follow bone growth. How long does it take fractures to heal? Factors deciding when a cast can come off include: Child’s age. Bone fractured. Fracture location. Young children heal faster than teens, teens heal faster than young adults, who heal faster than older adults. In young children most fractures heal in 4-6 weeks. However, teens generally take 6 weeks to heal, and adults can take much longer. Although your child is out of their cast, it may not be healed completely to return to all activities. Placing a splint is during this time is common. This typically gives them added protection for several weeks after their cast is removed - in case they forget their limitations. What if my child is still limping? Whether a child is in a walking or non-weight bearing cast, removing it often leaves them stiff and sore. Therefore many children will walk as though they still have a cast in place. In most cases this resolves in about three weeks. Regardless, if your child is still limping or walking abnormally after three weeks, contact the treating doctor. They may benefit from physical therapy or a repeat evaluation. (This article was original published in the July 2019 issue of South Reno Kids & Sports.)
Read More About Bone Fractures in Children Honest Expert Advice
-
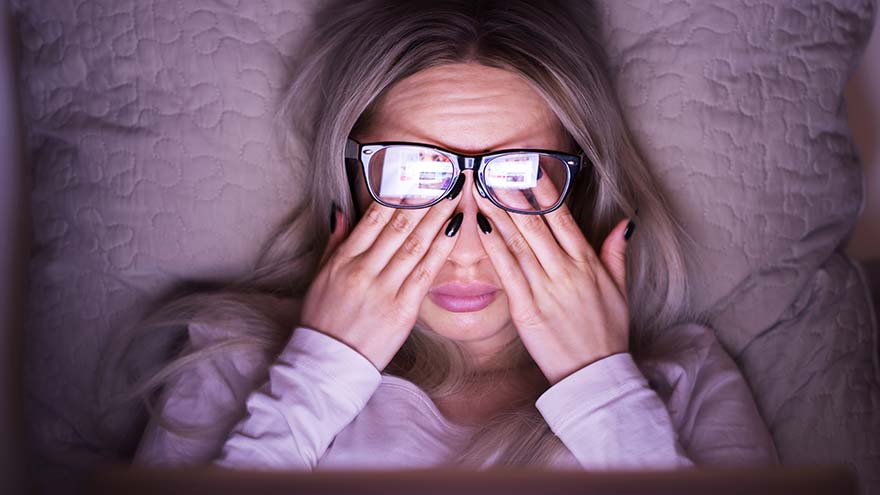
Are Blue Light Glasses Necessary?
Since the COVID-19 pandemic, more people are working from home than ever before, leading to a rise in digital screen time. Between spending eight or more hours staring at a computer screen, and some downtime hours spent looking at a smartphone or watching TV, it’s almost inevitable to feel some adverse effects at the end of a day. Blue Light Effects vs. Digital Eye Strain Blue light is all around us, and the most natural source comes primarily from sunlight. Other forms of blue light are artificial and emitted by digital screens including LED TVs, smartphones, tablets and computers. Surprisingly enough, research shows blue light can actually have health benefits such as promoting alertness, boosting memory and cognitive function, elevating mood and regulating circadian rhythm. However, studies indicate that an excess in blue light exposure can lead to depletion of melatonin production, a hormone that regulates our sleep cycles. In today’s eyewear industry, blue light glasses are one of the more popular items purchased by consumers. Companies who sell the glasses claim they help with reducing or eliminating digital eye strain, while also increasing natural melatonin secretion to get a good night’s sleep. Other than their slight yellow tint to filter out blue light, they mostly look like regular glasses and come in many different stylish frames. You can find blue light glasses through various eyewear retailers. Most adults have experienced digital eye strain. Common symptoms of digital eye strain include headaches, blurred vision, irritated eyes, and fatigue. Many believe that digital eye strain is caused by overexposure to blue light, but medical vision experts say that is not the case. “Digital eye strain is related to how we use our digital devices, not the blue light coming out of them,” says Mitchell Strominger, MD, a neuro and pediatric ophthalmologist with Renown Health. Do Blue Light Glasses Even Work? Since blue light glasses aren’t medically proven to help with digital eye strain, you’re probably wondering if they’re even worth using. “If you’re one to binge a TV show or scroll though social media before bedtime, the blue light from those digital screens can disrupt your circadian rhythm and cause you to lose sleep, which can ultimately lead to other adverse health effects,” says Dr. Strominger. “While more research is still needed, some studies have shown that blue light glasses may prevent melatonin suppression and increase quality of sleep. There is no harm in trying them out and seeing if they work for you.” As for preventing digital eye strain, Dr. Strominger shared several helpful tips: Try using the 20-20-20 rule, which entails looking away from your screen and looking at an object 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds. Sit at an arm’s length (about 25 inches) away from your screen. Adjust the brightness and contrast of your screen, especially before bedtime. There is a night mode setting on most smart phones you can use. Reduce your screen time whenever you can and give your eyes a break.