Search
-
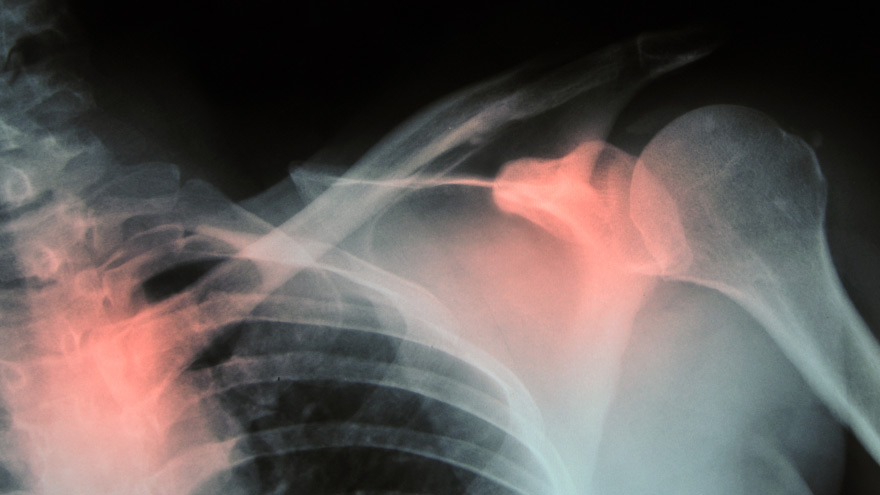
Prevent Osteoporosis: Take Control of Your Bone Health Today
Some risk factors associated with osteoporosis are out of your control. But you’re in luck, because some can be lessened by following simple tips. Below, Orthopedic Nursing Manager Katie McCarthy discusses the signs, symptoms and preventive measures. By Katie McCarthy, BSN, RN, ONC, Orthopedic Nursing Manager, Renown Health Osteoporosis is often called the silent disease, because it develops gradually for years with no clear signs or symptoms. And while some bone loss is expected as we age, osteoporosis is not a normal part of aging. So it’s important to start thinking about your bone health early. Bone is not just a lifeless scaffold for the body. It is living tissue that regenerates continually. Once we reach peak bone mass around age 25, we begin losing more bone than we produce, increasing the risk of developing osteoporosis — which literally means porous bone and points to a loss in bone density. In severe cases, normal everyday activities or movements, like hugging, can cause a fracture. After the first fracture you’re at higher risk for more, which can lead to a life of chronic pain and immobility. Bone fractures in the spine or hip are the most serious. Hip fractures can result in disability and even death — especially in older adults. Spinal fractures can even occur without falling. The vertebrae weaken to the point that they simply crumple, which can result in back pain, lost height and a hunched-forward posture. Osteoporosis: Uncontrollable Risk Factors Women are at greater risk of developing osteoporosis than men, and white and Asian women are at higher risk than black and Hispanic women. Other uncontrollable risk factors include: age; a family history of osteoporosis; certain genetic conditions; medications and medical treatments; eating disorders; a low body weight and small, thin frame; ethnicity; menopause: In fact, the lack of estrogen produced during menopause is largely responsible for a woman’s increased risk. Poor diet, tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, lack of exercise and an unhealthy weight also contribute to bone loss. Fortunately, those risk factors are in your control. Without symptoms, you can’t know if you’ve developed osteoporosis unless you get a bone density test or suffer a fracture. If you fall into a high-risk group, are over age 50 or have any concerns about your bone health, consult your doctor and find out if you need to be evaluated. Additionally, if either of your parents sustained hip fractures, you experienced early menopause or took corticosteroids for several months — a steroid often prescribed to relieve inflammation and arthritis — you’ll want to talk to your doctor about your bone health. If you test positive, your doctor will devise a treatment plan to match your needs, which will include lifestyle changes surrounding diet and exercise to build and strengthen weak bones. Medication to slow bone breakdown and build new bone may be prescribed, depending on the severity of your bone loss. If you’ve sustained a spinal fracture that is causing severe pain, deformity or is not responding to non-surgical treatment, your doctor may recommend surgery. Reduce Your Risk of Osteoporosis You can strengthen your bones now to prevent osteoporosis from starting. Here are some tips: Eat a diet rich in fruits and vegetables and low in caffeine, sodium and protein. Avoid soda, and talk to your doctor to make sure you’re getting enough calcium and vitamin D. Don’t smoke — it directly correlates with a decrease in bone mass. Smokers also take longer to heal from a fracture. Limit alcohol to two to three beverages per day. It interferes with the production of vitamins needed to absorb calcium and the hormones that help protect bones. Exercise three to four times each week — it’s key to healthy bones. Weight-bearing exercises like jogging, hiking and especially weight lifting build bone mass and density. There are aspects of the aging process we can’t control, but we can do something about bone loss and osteoporosis. Find out your risk, and show your bones a little TLC — you’re going to need them. This story was also published in the Reno Gazette-Journal’s Health Source on April 24, 2016.
Read More About Prevent Osteoporosis: Take Control of Your Bone Health Today
-
A True Joint Effort: Exercises to Prevent Knee Pain
Experiencing knee pain during exercise or while undertaking daily activities? The knee is the largest joint in our body, so it goes without saying a lot hinges on its functionality. Here are a few exercises to help. Is exercise a real pain in the knee for you? Does getting up in the morning require a few minutes for your knees to adjust to walking around? As it turns out, knee pain is common, and it can result from injury, overuse or the breakdown of cartilage over time. Often, this pain is a result of faulty mechanics in your body, according to Jessica Ryder, a physical therapist with Renown Physical Therapy and Rehab. “We see weakness at the hips causing a lot of stresses at the knee,” she says. Exercises that Alleviate Knee Pain Try these three exercise to strengthen your glute muscles and maintain proper alignment in your knees. Hip Lift Lie flat on your back with your knees bent and feet flat against the floor. Lift your hips into the air until your body is in a neutral position, then lower your hips back down. Repeat this motion several times until you feel a gentle burn in your glute muscles. Step Down Stand with one foot on a stair or step. Slowly bend your knee and drop the other foot toward the floor. Slowly extend back up to your starting position. While doing this exercise, it’s important to move slowly, maintain control and ensure that your knee is in line with your toes. Do as many reps as needed until you feel a small fatigue in your muscles. Repeat this exercise on the opposite leg. Side Step with Exercise Band Place an exercise band around your ankles. Stand in a slight squat and then take several steps to the side until you feel a small fatigue on the outside of your hips. While doing this exercise, keep your upper body still and focus the exercise to your hips. The band will try to move your knees toward each other Repeat in both directions. Hometown Health and Renown Health are proud to be the official insurance plan and healthcare partners of the Nevada Wolf Pack. Renown Physical Therapy and Rehab | 775-982-5001 Through outpatient physical, occupational and also speech therapy, Renown Physical Therapy and Rehab gives patients hands-on, individualized treatment. Our therapists use evidence-based methods to help patients return to an active, productive lifestyle. Learn More About PT
Read More About A True Joint Effort: Exercises to Prevent Knee Pain
-
Name-Brand Medication vs. Generic: What's the Difference?
Most prescriptions meds are available in generic form. Find out the similarities and differences between the two and how to determine whether a generic is right for you. Approximately 80 percent of prescriptions sold today are generics. If you’re taking a prescription medication, chances are it’s a generic form of the brand-name drug. But are you getting the same quality in a generic medication? Do generics measure up? The answer in most cases is yes — generics, just like branded products, are regulated by the Food and Drug Administration. “To have a generic product approved by the FDA, the generic manufacturer must prove that its product is bioequivalent to the branded product,” explains Adam Porath, PharmD, BCPS AQ-Cardiology, BCACP and Vice President of Pharmacy Services. Basically, it has to function the same. “Generic products are extremely well tolerated and will provide the same results as using a branded product,” Porath says. Here’s how generics are the same as name-brand prescriptions: Generic products contain the same active ingredients. They produce the same desired clinical effect and accompanying side effects. Generics come in the same form as their branded counterparts: pill, liquid or inhaler, for example. Release into the bloodstream matches the name brand in timing and strength. Here’s how they differ: Generics generally cost less. Federal law requires generics have different names and look different: shape, size, markings and color. Generics contain different inactive ingredients, like binders, fillers and artificial colors. Different side effects with generics can usually be attributed to these additions. Why do generics cost less? When pharmaceutical companies develop a new drug, they are paying for research, development, clinical studies, marketing — in some cases it can cost more than $800 million and take 10 to 15 years to develop a new drug. “The manufacturers of branded medication products have to recoup their research and development costs,” Porath says. So companies are granted a limited patent to sell their drug without the competition of generic counterparts. “When patent exclusivity ends, the market is open for any generic manufacturer to make a competing product with FDA approval.” Without the same startup costs, companies can sell generics at 80 to 85 percent less. And because more than one company can produce the same generics, competition drives prices even lower.
Read More About Name-Brand Medication vs. Generic: What's the Difference?
-
Copays vs. Coinsurance: Know the Difference
Health insurance is complicated, but you don't have to figure it out alone. Understanding terms and definitions is important when comparing health insurance plans. When you know more about health insurance, it can be much easier to make the right choice for you and your family. A common question when it comes to health insurance is, "Who pays for what?" Health insurance plans are very diverse and depending on your plan, you can have different types of cost-sharing: the cost of a medical visit or procedure an insured person shares with their insurance company. Two common examples of cost-sharing are copayments and coinsurance. You've likely heard both terms, but what are they and how are they different? Copayments Copayments (or copays) are typically a fixed dollar amount the insured person pays for their visit or procedure. They are a standard part of many health insurance plans and are usually collected for services like doctor visits or prescription drugs. For example: You go to the doctor because you are feeling sick. Your insurance policy states that you have a $20 copay for doctor office visits. You pay your $20 copay at the time of service and see the doctor. Coinsurance This is typically a percentage of the total cost of a visit or procedure. Like copays, coinsurance is a standard form of cost-sharing found in many insurance plans. For example: After a fall, you require crutches while you heal. Your coinsurance for durable medical equipment, like crutches, is 20% of the total cost. The crutches cost $50, so your insurance company will pay $40, or 80%, of the total cost. You will be billed $10 for your 20% coinsurance.
-
Health Insurance Terms Explained: Deductible and Out-of-Pocket Maximum
Health insurance might be one of the most complicated purchases you will make throughout your life, so it is important to understand the terms and definitions insurance companies use. Keep these in mind as you are comparing health insurance plan options to choose the right plan for you and make the most of your health insurance benefits. One area of health insurance that can cause confusion is the difference between a plan's deductible and out-of-pocket maximum. They both represent points at which the insurance company starts paying for covered services, but what are they and how do they work? What is a deductible? A deductible is the dollar amount you pay to healthcare providers for covered services each year before insurance pays for services, other than preventive care. After you pay your deductible, you usually pay only a copayment (copay) or coinsurance for covered services. Your insurance company pays the rest. Generally, plans with lower monthly premiums have higher deductibles. Plans with higher monthly premiums usually have lower deductibles. What is the out-of-pocket maximum? An out-of-pocket maximum is the most you or your family will pay for covered services in a calendar year. It combines deductibles and cost-sharing costs (coinsurance and copays). The out-of-pocket maximum does not include costs you paid for insurance premiums, costs for not-covered services or services received out-of-network. Here's an example: You get into an accident and go to the emergency room. Your insurance policy has a $1,000 deductible and an out-of-pocket maximum of $4,500. You pay the $1,000 deductible to the hospital before your insurance company will pay for any of the covered services you need. If you received services at the hospital that exceed $1,000, the insurance company will pay the covered charges because you have met your deductible for the year. The $1,000 you paid goes toward your out-of-pocket maximum, leaving you with $3,500 left to pay on copays and coinsurance for the rest of the calendar year. If you need services at the emergency room or any other covered services in the future, you will still have to pay the copay or coinsurance amount included in your policy, which goes toward your out-of-pocket maximum. If you reach your out-of-pocket maximum, you will no longer pay copays or coinsurance and your insurance will pay for all of the covered services you require for the rest of the calendar year.
Read More About Health Insurance Terms Explained: Deductible and Out-of-Pocket Maximum
-
Understanding "In-Network" and "Out-of-Network" Providers
When finding a provider to receive your health services, you've probably heard the terms "in-network" and "out-of-network" when it comes to your health plan. But what do these terms mean for a patient? And why should you be aware if a provider is out-of-network? What does it mean when a provider is "in-network" with a health plan? A provider is a person or facility that provides healthcare. When a provider is in-network it means there is a contractual agreement with that health plan regarding the rates for services. The provider will accept negotiated rates for services from the insurance. This means a patient will typically pay less for medical services received and is less likely to receive surprise bills. What does it mean when a provider is "out-of-network" with a health plan? Providers that are out-of-network are those that do not participate in that health plan's network. The provider is not contracted with the health insurance plan to accepted negotiated rates. This mean that patients will typically pay more or the full amount for the service they receive. Why should patients see in-network providers? Seeing an in-network provider for medical services can significantly reduce your medical expenses. Remember that in-network providers have a contractual agreement for negotiated rates with the health plan, so they cannot charge you more than that negotiated rate for a service. Seeing an in-network provider will always ensure any costs you do incur (copays or co-insurance) are applied to your health plan's deductible and out-of-pocket maximum (out-of-network costs don't apply to these amounts). To find the amounts you will pay for specific services, you can check your health insurance plan's Summary of Benefits. What is the best way to find which providers are in-network with a patient's health plan? Most health insurance companies offer multiple ways to find if a provider is in-network. To find the most accurate benefit information from your health plan, you can: Call their Customer Service department Check their website for their online provider directories If offered, check your online member portal.
Read More About Understanding "In-Network" and "Out-of-Network" Providers
-
3 Ways to Switch to a Medicaid Plan Accepted at Renown
Medicaid plays a significant role in our health care system and is the nation’s public health insurance program. In addition, this program is the predominant source of long-term care coverage for Americans. Renown Health is contracted with two Medicaid plans: Molina and Anthem. If you currently have a different plan but want to change to one that Renown accepts, you can request to change plans during the open enrollment period from January 1 to March 31. Request to change your Medicaid plan in one of three ways: Request a change to your plan, or managed care organization (MCO), by reviewing the available MCO plans online at bit.ly/MCOPlansNV and filling out the form on the webpage. Email Nevada Medicaid to ask for a plan change and include your name, Medicaid ID and the names and Medicaid IDs of any dependents in your home: MCORedistribution@dhcfp.nv.gov. Call your local Medicaid district office at 775-687-1900 (northern Nevada) or 702-668-4200 (southern Nevada) to ask about changing your plan. For more information about the Medicaid plans accepted at Renown Health, please visit: Anthem Molina Healthcare Renown Health accepts most insurances, but please visit the link below for the full list. Click here for all accepted plans
Read More About 3 Ways to Switch to a Medicaid Plan Accepted at Renown
-
Generic Drugs – What You Need to Know About Them
Without a doubt, taking medications can not only be expensive, but also confusing. In the United States, generic prescriptions are widely used, with 9 out of 10 people choosing them over a name brand. Pharmacists are a great resource to help us understand the benefits and side effects of any medication. We asked Adam Porath, PharmD, Vice President of Pharmacy at Renown Health, to answer some common questions about generic drugs. What is a generic drug? A generic drug has the same active ingredients of brand-name drugs. Brand-name drugs have a patent (special license) protecting them from competition to help the drug company recover research and development costs. When the patent expires other manufacturers are able to seek approval for a generic drug. However, the color, shape and inactive elements may be different. Per the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA), a generic medicine works in the same way and provides the same clinical benefit as its brand-name version. Why do they cost less? Generic drug makers do not have the expense of costly development, research, animal and human clinical trials, marketing and advertising. This savings is passed on to the public. Also after a patent expires, several companies will compete on a generic version of a drug, further driving down prices.
Read More About Generic Drugs – What You Need to Know About Them
-
Pharmacists Answer Questions about the COVID-19 Vaccines
Vaccines that provide protection against the COVID-19 virus are bringing us closer to the end of this deadly pandemic. Two different COVID-19 vaccines are currently available in the U.S. today: one from Pfizer and the other from Moderna. Kate Ward, PharmD, BCPS, Director of Clinical Pharmacy at Renown Health and Adam Porath, PharmD, Vice President of Pharmacy at Renown, share what you need to know about these vaccines. When two COVID-19 vaccines were approved by the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) in December 2020, it was cause for celebration. Why? Because according to the CDC, the vaccines are 94 percent or more effective in providing protection against the COVID-19 virus! Many people are seeking information about the new Moderna and Pfizer vaccines. Below, our pharmacy leaders provide answers to some commonly asked questions. How do the COVID-19 Vaccines Work? The Pfizer and Moderna vaccines are both mRNA vaccines that help your immune system develop antibodies against the COVID-19 virus. The vaccines use messenger RNA, or mRNA, to show our bodies’ protein-making cells how to make the spike proteins of the COVID-19 virus. Our immune system reacts to these spike proteins by creating antibodies that can recognize and destroy them. So when a person is exposed to the virus in the future, they will be less likely to get sick. What are the Differences between the Pfizer and Moderna Vaccines? The Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines are very similar, with just a few small differences worth noting. The main difference between the two vaccines is when you should receive your follow-up dose. Patients who receive a first dose of Pfizer should receive their second dose about three weeks later. Those who receive a first dose of Moderna should receive their follow-up vaccination roughly four weeks after their first dose. People 18 years and older can receive the Moderna vaccine while people 16 years and older can receive the Pfizer vaccine. Dosage for the Moderna vaccine is 0.5 ml (100 mcg). Dosage for the Pfizer vaccine is 0.3 ml (30 mcg).
Read More About Pharmacists Answer Questions about the COVID-19 Vaccines