Search
-
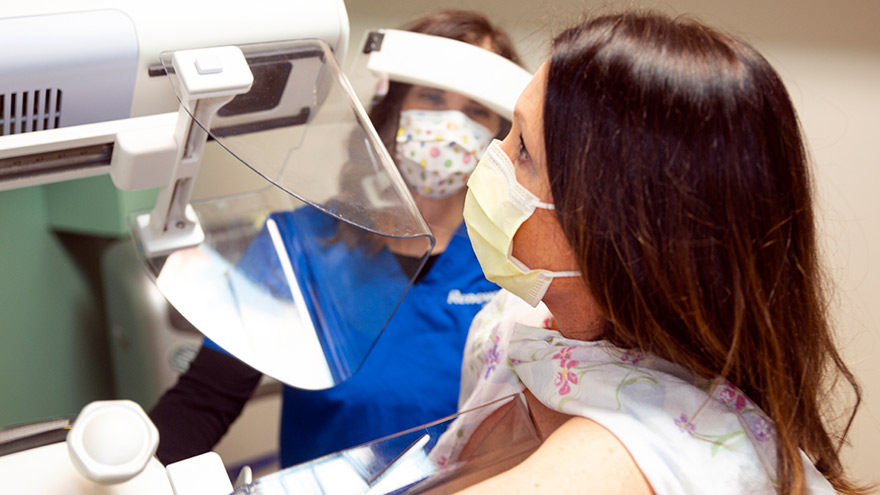
3D vs Whole Breast Ultrasound Which is Right for You
Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in women in the U.S. That’s why early detection is so important. Dr. George Krakora, a radiologist with Renown Institute for Cancer, explains what to watch for and how new technology can lead to early detection. Most women know the importance of breast health and staying current with annual breast exams, but may not know that both screening guidelines and technology is evolving. So we asked George Krakora, MD, a radiologist for the Renown Institute for Cancer, what every woman should know about breast cancer detection and which screening method is right for them. First off, when should women start getting breast exams? Generally, women should start getting breast exams using mammography or ultrasound after they turn 40 years old. But we also want women ages 18 to 39 to talk to their primary care provider and ask for what’s called a formal risk assessment to see if screening is needed sooner. And you want to make sure your care provider is giving you a breast exam starting at age 25. It’s also a good idea to be familiar with how your breasts look and feel so you can report any changes to your care provider. What are the risk factors for breast cancer? Are there any preventive steps women can take? There a few risk factors you can’t control, like your age, family history of breast or other cancers, and if you have dense breast tissue. Your risk for breast cancer increases as you get older, and most breast cancers are diagnosed after age 50. Knowing your family history is important because a history of cancer and shared lifestyle can raise your risk. Your breast density can also increase your risk: Women with high breast density are four-to-five times more likely to get breast cancer than women with low breast density. But the good news is there are quite a few things you can do to prevent breast cancer, like not smoking, watching your alcohol intake, and maintaining a healthy weight with good diet and exercise. There are a lot of newer screenings out today. What is the difference between 2-D and 3-D mammography? In a 2-D mammogram, the tech takes X-rays of the breast. These pictures can show the radiologist if there are any lumps or tumors you might not be able to feel. In 3-D mammography, the process is largely the same but more X-rays are taken and it takes a few seconds longer for each image. This kind of exam detects 41 percent more cancers and reduces the number of false-positive results given to patients. This improvement in technology is great for both patients and their care providers. 3-D mammography provides better images of the breast, which allow doctors to more clearly diagnose and avoid false positives, especially in women with dense breast tissue. And what about a whole breast ultrasound. What is that? A whole breast ultrasound uses sound waves to detect cancerous tumors in the breast without using any radiation — it’s an ultrasound just like pregnant women get to check up on their baby. And the exam only takes about 20 minutes. We recommend these exams for patients whose mammograms have shown that they have dense breast tissue. Dense breast tissue can make it harder for doctors to see any abnormalities, lumps or tumors in a mammogram, so this technology ensures better early detection.
Read More About 3D vs Whole Breast Ultrasound Which is Right for You
-
Cervical Cancer Screenings Can Reduce Risk of Cancer
According to the American Cancer Society, approximately 14,100 new cases of invasive cervical cancer will be diagnosed, and 4,280 women will die from cervical cancer. However, cervical cancer is preventable with regular screening tests and the HPV vaccine. It’s important to note that medical advances have allowed progress in diagnosing and treating cervical cancer. While it used to be one of the most common causes of cancer death for American women, the incidence of death has significantly declined. What to Know About the HPV Vaccine HPV vaccination is the best way to prevent cervical cancer and is recommended for all youth starting as early as age 9, or for teens and adults up to age 45 who didn’t start or finish the series. In Nevada, only 50.1% of teens ages 13-17 have been vaccinated for HPV. There are 13 types of HPV, and the vaccine Gardasil 9 protects against 9 of those HPV strains, greatly reducing the incidence of cervical cancer among vaccinated individuals. What to Know About Cervical Cancer Screenings The CDC says the most important thing you can do to help prevent cervical cancer is to have regular screening tests starting at age 21. And there are two common tests that can detect early stages of cervical cancer (or precancer) and improve health outcomes. The pap test (or pap smear). This screening looks for precancers. Women should begin getting pap smears when they’re 21. The human papillomavirus (HPV) test looks for the virus that can cause these cell changes. Cervical Cancer Screening Schedule The American Cancer Society offers the following guidelines for screenings: All women should begin cervical cancer screening at 21. Women between 21 and 29 should have a pap test every three years. Beginning at 30, the preferred way to screen is with a pap test combined with an HPV test every five years. This is called co-testing and should continue until age 65. A pap test (or pap smear) is performed during a regular screening appointment to look for precancers, cell changes on the cervix that might become cervical cancer if they are not evaluated or appropriately treated. Typically outpatient procedures can reduce the risk of long-term health impacts that prevent pre-cancerous cells from becoming cancer cells. Women over 65 who have had regular screenings in the previous ten years should stop cervical cancer screening as long as they haven’t had any severe precancers found in the last 20 years. How to Get Screened Request an appointment with your primary care physician or OBGYN to schedule a screening.
Read More About Cervical Cancer Screenings Can Reduce Risk of Cancer
-
Why are Annual Exams & Routine Screenings Important?
March is Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month, and we want you to receive the best preventative care possible. Early detection can help prevent serious illness, yet many people still choose to skip their annual exams and routine screenings. Bonnie Ferrara, MD, MPH, Section Chief for Primary Care at Renown Medical Group, further explains the importance of this simple, easy way to stay healthy. Why are annual exams so important? The benefits of early detection and prevention to save lives and reduce the impacts of disease have been proven. These exams are the perfect opportunity to get your health questions answered. “This is your chance to sit down with your provider and talk about your overall health and your family’s health history as well as your concerns for the future,” says Bonnie Ferrara, M.D., family medicine. “It’s the opportunity for your provider to talk with you about your lifestyle, tobacco use, exercise and alcohol use, all of which make a difference in your future longevity.” The annual wellness exam is also an ideal time for most adult patients to discuss health screenings. In addition, these visits are the perfect time to address issues that may not directly relate to a particular medical problem or immediate illness. A good rule of thumb is to schedule these appointments around your birthday each year to make sure you and your provider are both updated on your care. Why would you need an annual exam if you aren’t feeling sick? According to Dr. Ferrara, seeing your care provider when you aren’t sick is one of the best times. “It is better if you try to arrange this visit when you are not feeling ill,” she says. “It is an opportunity to talk about wellness. Not only how to contribute to your wellness but also the changes that you can make that will make huge dividends in the future for your wellness. In addition, it allows us to do some education about what to expect in the coming years as far as your health and lifestyle changes.” What can you expect at an annual exam? Annual exams usually check your: History – lifestyle behaviors, health concerns, vaccination status, family medical history Vitals – blood pressure, heart rate, respiration rate and temperature General appearance – your care provider can find out a lot about you just by watching and talking to you Dr. Ferrara adds, “If this is a Medicare annual wellness exam, it is an opportunity to talk to your provider about depression and dementia as well as be tested for those.” You can also leverage your annual exam to speak to your provider about managing your chronic health problems. "As a provider, these visits give us the opportunity to hear how the medications and lifestyle changes we have recommended are working and if you are having problems with these, we have the opportunity to make suggestions of how to do things better for the future," Dr. Ferrara.
Read More About Why are Annual Exams & Routine Screenings Important?
-
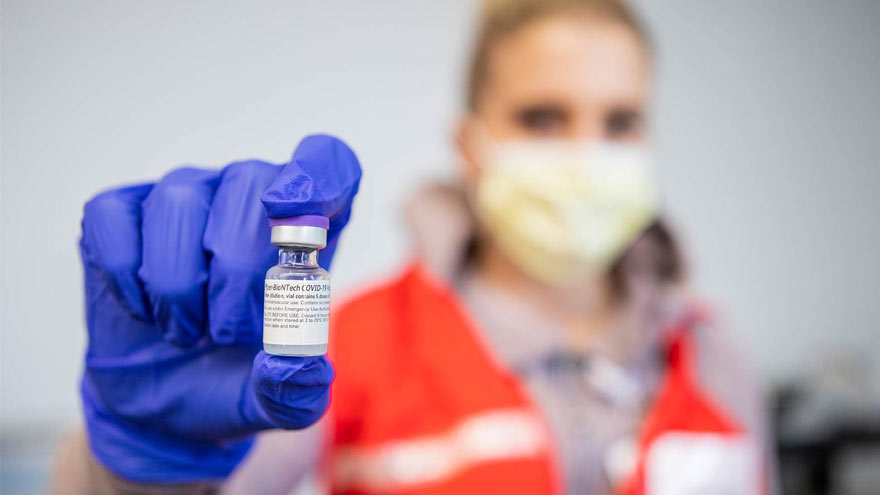
COVID-19 Booster Shots, What You Need to Know
Getting the COVID-19 booster is the best way to protect yourself from severe illness or death due to COVID-19, and both the CDC and the FDA have approved booster shots for people ages 18 and older. So, with the holidays right around the corner and infection rates on the rise both in Nevada and nationally, the best thing you can do to prevent the continued spread of this deadly virus is to get boosted today. The Basics: Who: It is recommended that everyone 18 years or older get a COVID-19 booster shot. When: At least 6 months after completing your primary COVID-19 vaccination series. What: Any of the COVID-19 vaccines authorized in the United States. The CDC allows for mix and match dosing for booster shots. How: To make an appointment for your COVID-19 vaccine booster, please visit vaccines.gov today. Appointment Reminders: Don’t forget to bring your CDC vaccination record card to your appointment. Refresh yourself on the potential side effects and remember that these are normal signs your body is building up protection. Commonly Asked Questions: Q: Does anything change if I received the Johnson & Johnson as my first COVID-19 vaccine? A: If you received the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine, you are elidable for a booster two months after completing your primary vaccine. Q: Is the formula the same for the boosters as it was for the primary vaccine? A: COVID-19 booster shots are the same formulation as the current COVID-19 vaccines. However, in the case of the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine booster shot, it is half the dose of the vaccine people get for their primary series. Q: Am I still considered “fully vaccinated” if I don’t receive a COVID-19 booster shot. A: Yes, everyone is still considered fully vaccinated two weeks after their second dose in a two-shot series, such as the Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna vaccines, or two weeks after a single-dose vaccine, such as the J&J/Janssen vaccine. All information courtesy of the Center for Disease Control and Prevention. All information courtesy of the Center for Disease Control and Prevention
Read More About COVID-19 Booster Shots, What You Need to Know
-
Pharmacists Answer Questions about the COVID-19 Vaccines
Vaccines that provide protection against the COVID-19 virus are bringing us closer to the end of this deadly pandemic. Two different COVID-19 vaccines are currently available in the U.S. today: one from Pfizer and the other from Moderna. Kate Ward, PharmD, BCPS, Director of Clinical Pharmacy at Renown Health and Adam Porath, PharmD, Vice President of Pharmacy at Renown, share what you need to know about these vaccines. When two COVID-19 vaccines were approved by the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) in December 2020, it was cause for celebration. Why? Because according to the CDC, the vaccines are 94 percent or more effective in providing protection against the COVID-19 virus! Many people are seeking information about the new Moderna and Pfizer vaccines. Below, our pharmacy leaders provide answers to some commonly asked questions. How do the COVID-19 Vaccines Work? The Pfizer and Moderna vaccines are both mRNA vaccines that help your immune system develop antibodies against the COVID-19 virus. The vaccines use messenger RNA, or mRNA, to show our bodies’ protein-making cells how to make the spike proteins of the COVID-19 virus. Our immune system reacts to these spike proteins by creating antibodies that can recognize and destroy them. So when a person is exposed to the virus in the future, they will be less likely to get sick. What are the Differences between the Pfizer and Moderna Vaccines? The Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines are very similar, with just a few small differences worth noting. The main difference between the two vaccines is when you should receive your follow-up dose. Patients who receive a first dose of Pfizer should receive their second dose about three weeks later. Those who receive a first dose of Moderna should receive their follow-up vaccination roughly four weeks after their first dose. People 18 years and older can receive the Moderna vaccine while people 16 years and older can receive the Pfizer vaccine. Dosage for the Moderna vaccine is 0.5 ml (100 mcg). Dosage for the Pfizer vaccine is 0.3 ml (30 mcg).
Read More About Pharmacists Answer Questions about the COVID-19 Vaccines
-
Reno Widow Inspires New Visitor Policy for Renown
Renown Health is one of the country’s first health systems to lift visitor restrictions for patients with COVID-19 and encourage the family to be at the patient’s bedside. Read Darlene and Dave’s story to understand why we’re updating our visitor policy. Dave and Darlene Randolph found joy in exploring antique shops and garage sales to find damaged or discarded vintage pieces. Dave would spend many hours scraping, cleaning, sanding, and refinishing items, transforming them into functional, beautiful pieces of furniture. Every piece in their home rekindles a memory and has a story to tell. On Thanksgiving, when Dave was too ill to gather around their antique dining room table, Darlene called the ambulance. Ailing with COVID-19 for two weeks, Dave had not been improving. When the EMTs reached her home and asked Darlene what underlying conditions he had, she said, “all of them.” David was seriously ill. Hospitalized for COVID-19, their communications options were limited. The only way Darlene could communicate with Dave was on a video call or by telephone. Dave spent 17 days hospitalized at Renown Regional Medical Center in Reno. Darlene spent 17 days waiting by the phone for more information on his condition. Darlene said he had “up days and down days,” but thought he might be home, sitting at their antique dinner table for Christmas. Sadly, Dr. David Randolph lost his battle with COVID-19 on December 13, 2020, and died as he slept in a hospital bed. When Darlene wrote his obituary for the newspaper, she gave thanks to the “tremendous nurses and doctors at Renown Regional Medical Center, for providing his care during a time when the family could not be with him.” Taking Action to Inspire Change Darlene wished she could have been there. Over their 45-year marriage, she had always been there. Darlene said, “I had always been at his bedside, as his advocate, to help communicate and straighten things out.” As a registered dietician, she worked in hospitals, knew the protocol, and knew that Renown had a restricted visitor policy to stop the virus’s spread- to other patients, staff, and their family members. Still, she wished she could have spent more time with him. On Christmas Eve, she sat down and wrote to Renown leadership. “As the wife of a COVID patient who recently passed away in your hospital, I want to express my thanks to you and your staff for the care he received in the last days of his life. I am aware that the nurses and staff are working under dangerous conditions and risking their health and lives by caring for multiple COVID patients. The staff is gracious, concerned, and doing everything they can.” She continued, “I know procedures are changing every hour to try to stay ahead of this dangerous virus, and I am sharing my experiences, hoping they will be helpful when establishing policies that impact families.” Darlene explained that despite receiving assurances that Dave’s nurse or a doctor would call daily, sometimes they would forget. She explains in her letter, “how important it is, in these times when the family cannot visit, and has only infrequent communication and is anxiously waiting at home for information about their loved one, how much it means to get a call from someone caring for him at the hospital. If there is a way you can help assure nurses have time to make calls or assist patients in making calls because it is an important part of patient care.” A Person-Centered Visitor Policy After receiving her letter, Renown leadership called Mrs. David Randolph to thank her, offer his sympathies and ask if Renown could help in any way. Darlene asked if he might reconsider allowing families to visit hospital patients during treatment for COVID-19. As the COVID-19 situation has evolved, the policy has as well. Renown hospitals and medical practices now encourage limited visitors for all patients, including those diagnosed with COVID-19. Renown also has extra safety measures to protect the health of patients, visitors and healthcare employees. Darlene is very pleased that her letter inspired this shift in visitor policies for patients with COVID-19. She says, “I have always tried to think of ways I could help other families. Especially those senior couples where one has been hospitalized and the other is home. My wish is to help others.” Renown Health Visitor Policy Renown Health patients may identify two healthy adult “patient supporters” to accompany them on their hospital stay. For more details, visit our Patient Supporter Guidelines page.
Read More About Reno Widow Inspires New Visitor Policy for Renown
-
COVID-19 Vaccine Expert Advice
With front-line workers receiving the first COVID-19 vaccinations, many of us are feeling hope, but also worry. As a result, we are joining with the Ad Council, the COVID Collaborative, HHS, CDC and NIAID (along with top health and medical organizations) to address your vaccine concerns and questions. Will the vaccine be available to everyone in Nevada? The Nevada Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) is collaborating with health systems about the use of initially available, limited supplies of COVID-19 vaccines. They will provide guidance on the prioritization order of who will receive the vaccine. This will be based on available quantities, high-risk locations of work and certain other risk factors, and recommendations and guidance for public health agencies. The CDC has provided guidance to initially focus on the following groups: Healthcare personnel likely to be exposed to or treat people with COVID-19, nursing home residents and others in institutional settings; People at risk for severe illness from COVID-19 due to underlying medical conditions; People 65 years of age and older; Other essential workers. I worry the vaccine has been rushed The U.S. national vaccine safety system ensures that all vaccines are as safe as possible, and because vaccines are given to millions of healthy people to prevent serious diseases, they’re held to very high safety standards. COVID-19 vaccines are undergoing a rigorous development process that includes vaccinating tens of thousands of people who participate in a study to generate the needed clinical data. These clinical trials generate scientific data for the FDA to determine the safety and efficacy of each vaccine. It’s worth noting that the clinical studies to establish the safety and efficacy of the Covid-19 vaccines were as big and thorough as recent studies for other licensed vaccines (for example, the shingles vaccine). I'm concerned about the vaccine's side effects The most common side effects are very similar to those seen with most vaccines, such as: sore arms, fevers, and tiredness within 72 hours after the vaccine. These side effects usually mean that the vaccine is generating an immune response, indicating it is working. Short-term side effects observed in the leading COVID-19 vaccine trials include: Injection site pain and redness Fatigue Muscle aches and pains Joint pain Headache I’m afraid I’ll get COVID-19 from the vaccine None of the authorized and recommended COVID-19 vaccines, or COVID-19 vaccines currently in development in the United States, contain the live virus that causes COVID-19. This means that a COVID-19 vaccine cannot make you sick with COVID-19. Can children receive the COVID-19 vaccine? Not at the moment. In early clinical trials for various COVID-19 vaccines, only non-pregnant adults at least 18 years of age participated. However, clinical trials continue to expand those recruited to participate. The groups recommended to receive the vaccines could change in the future. As of now, it is recommended that children do not receive the vaccine. More information will be available from the vaccine manufacturers. I do not believe vaccines are effective Both this disease and the vaccine are new. We don’t know how long protection lasts for those who get infected or those who are vaccinated. What we do know is that COVID-19 has caused very serious illness and death for a lot of people. If you get COVID-19, you also risk giving it to loved ones who may get very sick. Getting a COVID-19 vaccine is a safer choice. The FDA is responsible for making sure that, just like any other medications, any FDA-authorized or approved COVID-19 vaccines are safe and they work. The EUA (Emergency Use Authorization) will not be provided if the FDA feels that the vaccine is unsafe. I can't get vaccines to due to a medical condition Adults of any age with certain underlying medical conditions are at increased risk for severe illness from the virus that causes COVID-19. mRNA COVID-19 vaccines may be administered to people with underlying medical conditions provided they have not had a severe allergic reaction to any of the ingredients in the vaccine. The following information aims to help people in the groups listed below make an informed decision about receiving the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. It is extremely important to speak with your doctor regarding your specific medical condition, and always follow their strict advice regarding the COVID-19 vaccine, or any other vaccines. Sources: Renown COVID-19 Ad Council COVID Collaborative U.S. Department of Health & Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease
-
Monkeypox: A Renown Expert Weighs In
Renown Health is closely following the national outbreak of the monkeypox virus and urging healthcare providers to be alert for patients with illnesses associated with a rash. In working with the Washoe County Health District (WCHD), Renown is closely monitoring the spread of monkeypox in the community and looking to prevent and reduce the spread of monkeypox. To help to ease worries, we consulted with Paul De Leon, Infection Preventionist at Renown Health. What Exactly is Monkeypox? Monkeypox is a rare viral illness caused by the monkeypox virus — the same family of viruses that causes Smallpox. Although symptoms are similar to Smallpox, monkeypox symptoms are milder and rarely fatal. However, it's important to mention that this virus can be more severe for these susceptible groups: Immunocompromised Pregnant women A fetus or newborn baby Women who are breastfeeding Young children Those with severe skin diseases such as eczema How is Monkeypox Transmitted? The monkeypox virus is not easily transmitted but occurs through sustained person to person close contact with an infected individual. Monkeypox can also be transmitted through direct contact with infectious rash, scabs, or body fluids. Monkeypox can also be spread through prolonged intimate physical contact, such as kissing, cuddling or sex. Lastly, monkeypox can be spread through contaminated linens or bedding. Transmission through respiratory secretions is uncommon but has been reported after prolonged face-to-face contact with symptomatic individuals. In addition, pregnant women can spread the virus to their fetuses through the placenta. Monkeypox Testing If you think you have monkeypox, contact your primary care physician or other medical providers to obtain testing. Notify the provider ahead of time before entering the physical office. Signs & Symptoms This current outbreak of West African monkeypox does not have the typical presentation of classic monkeypox. Symptoms usually appear one to three weeks after infection and include: Pimple-like rash or blisters on the face, inside the mouth, and on other areas of the body, like the hands, feet, chest, genitals, or anus. The rash will go through serval stages, including scabs, before healing and may be painful or itchy. Other symptoms of monkeypox can include: Fever Headache Muscle aches and backache Swollen lymph nodes Chills Exhaustion Respiratory symptoms such as sore throat, nasal congestion, or cough Symptoms of monkeypox may occur before or after a rash with some individuals only report experience a rash. Individuals with monkeypox are infectious once symptoms begin and remain infectious until lesions form scabs, scabs fall off, and a fresh layer of skin forms. The illness typically lasts 2-4 weeks.
-
8 Important Health Screenings for Men
Unfortunately, men are less likely to visit their doctor for exams, screenings, and consults than women. So with the help of Bonnie Ferrara, MD of Renown Health, we've put together a list of eight screenings to help men stay on top of their health game. 1. Blood Pressure Tests Ages 20+ Blood Pressure tests measure the pressure in your arteries as your heart pumps. Biennial (every two years) checks are recommended if you have normal blood pressure or more frequently if you have high blood pressure (hypertension) or low blood pressure (hypotension). The United States Preventative Services Taskforce cites normal blood pressure below 120 systolic (top number) and 80 diastolic (bottom number). 2. Cholesterol Screening Ages 20+ High levels of cholesterol increase your risk of stroke and heart disease. A simple blood test will help your healthcare provider determine your numbers and if you're at risk. If you have a family history of diabetes or heart disease, you may need yearly screenings. But, again, your doctor can provide the best course of action.
-
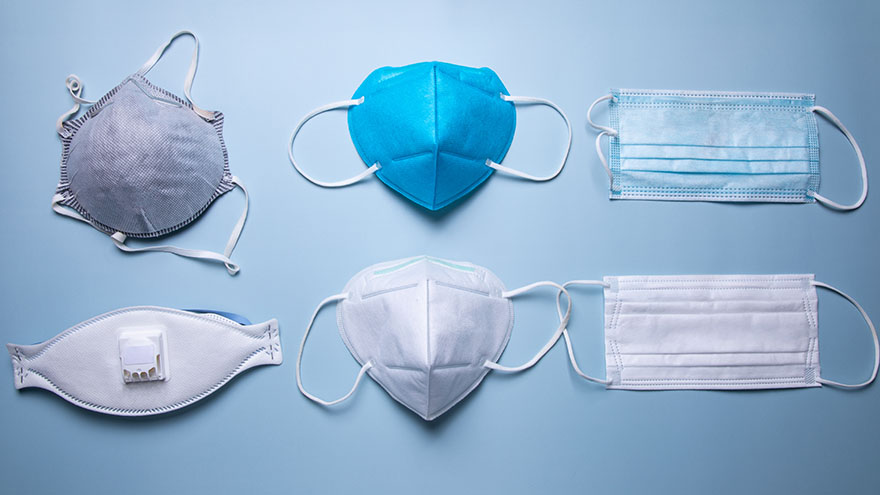
Avoid Counterfeits and Find the Right Protective Mask with This Helpful Guide
To better protect our patients, visitors and employees, cloth masks are no longer allowed at Renown facilities. Surgical masks, KN95 and N95 masks are allowed at Renown facilities. Appropriate face masks will be provided for visitors and patients who need one. With recent surges in the infectious COVID-19 omicron variant, many have sought to upgrade their face masks. But, let’s face it, shopping for face masks with adequate protection can be a challenge, especially considering the countless variations and the rise of counterfeit masks. Follow our straightforward guide below which includes some common red flags to help you discern between a high-quality face mask that provides proper protection and those that may be counterfeit. Types of Masks Qualities of a Real N95 Respirator Mask According to the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), N95 approved masks form a tight seal around your face and include a disposable respirator that removes particles including bacteria, viruses and dust as you breathe. N95 masks that are NIOSH approved undergo strict quality assurance and performance requirements to ensure mask respirators filter out up to 95% of hazardous particles. As a rule of thumb, N95 masks will not have ear loops, commonly used in cloth or surgical face masks. N95 respirators will contain two elastic bands or head straps that fasten behind the head, one securing the crown of the head and the other resting at the base of the neck, providing a snug fit and seal. Some other common signs that an N95 might be counterfeit include lack of all proper labeling, misspellings of NIOSH, decorative fabric and claiming to be approved for children. Currently, masks in adult sizes are the only masks to undergo NIOSH’s quality assurance and testing process. Respirators approved by NIOSH will include a testing certification (TC) approval number and will contain specific labeling on the facepiece of your mask. Find a full list of Center for Disease Control (CDC) and NIOSH requirements here. Identifying Real KN95 Respirator Masks Often preferred due to comfortability, the KN95 respirators were initially designed to meet Chinese standards for medical masks. Firstly, if a KN95 mask claims to be approved by the CDC, it is counterfeit as the CDC and NIOSH do not support any respiratory protective devices according to international standards. However, when KN95 masks are fitted and worn appropriately they do provide more protection than disposable masks. Legitimate KN95 masks will display a manufacturer number, GB2626-2019, ensuring accordance with current Chinese respirator standards for all masks made after July 1, 2021. Unlike N95 masks, it is important to note that KN95 masks are available in children's sizes. You might run into KN95 masks claiming to be “FDA (Food and Drug Administration) approved” or “FDA-registered,” but be aware that this does not mean much and is a misleading statement. What this indicates is that a mask maker has submitted paperwork to the FDA, but the product has not been thoroughly tested for proper filtration and protection. Surgical Masks Medical procedure masks often referred to as surgical or disposable masks vary in their protection according to a variety of factors including fit and filtration. The CDC defines medical procedure masks as “variably shaped, including flat pleated, cone-shaped, or duck-bill. Medical procedure masks are loose and are not expected to provide a reliable level of protection against airborne or aerosolized particles as N95 respirators regulated by the National Institute of for Occupational Safety and Health.” However, these types of masks provide more protection than cloth masks and are certainly better than wearing no mask at all. Often popular due to their level of comfort and cost-effectiveness, surgical masks can be knotted in the ear loop areas to provide a tighter seal and can be layered for additional filtration. Depending upon your budget and level of comfortability and protection, one variation of mask may suit you over another. Please remember to do your part in limiting the spread of COVID-19 and wear a surgical mask, KN95 or N95 mask when visiting Renown facilities.
Read More About Avoid Counterfeits and Find the Right Protective Mask with This Helpful Guide
-
Lung Cancer Screening and Early Detection
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in both men and women in the U.S. The good news is the five-year survival rate increases dramatically if lung cancer is treated before spreading to other parts of the body. Julie Locken, MD, of Renown Health Imaging, explains more. What are the signs and symptoms of lung cancer? As you might expect, most lung cancer symptoms appear in the chest and can affect your breathing. Watch for signs such as: Persistent cough Constant chest pain Shortness of breath Wheezing Bloody or rust-colored phlegm Hoarseness Swelling of the neck Pain or weakness in the shoulder, arm or hand Recurring pneumonia, bronchitis or other lung infections Loss of appetite and loss of weight can also be signs of lung cancer That said, there are usually no symptoms in the early stages of lung cancer, which means getting screened can truly be a lifesaver. If you have a history of smoking, you should get screened as a precaution. What are the risk factors of lung cancer? Around 80% of lung cancer cases stem from a history of smoking tobacco. But there are other known causes, such as secondhand smoke, radon, asbestos and diesel exhaust. It’s important to do what you can to eliminate exposure to all of these to reduce your lung cancer risk. People with an immediate relative – a parent, sibling or child – diagnosed with lung cancer and people between 50 and 80 years old are also at higher risk and may need to consider screening. People who are at the highest risk are those with a history of smoking tobacco, particularly smokers who averaged one pack of cigarettes per day for 20 years or more, as well as former heavy smokers who quit in the last 15 years.
-
Ladies! Get Screened for Breast Cancer
Early detection is a significant piece of the breast cancer puzzle. Susan Cox, Renown Health Director of Cancer Operations, discusses what you need to watch for and how the latest technology can help detect potential cancer sooner. When should women start getting breast exams? It depends on risk factors: Average-risk women: Most medical organizations recommend the first mammogram between 40 and 44. Higher-risk women: Dependent on their high risk, which will dictate when they start screening, but generally around the age of 30 and not before 25 years old.